
This demonstrates that, for every Cardinal model they sell, they will have $60 to contribute toward covering fixed costs and, if there is any left, toward profit. The contribution margin ratio is just one of many important financial metrics used for making better informed business decisions. The ratio can help businesses choose a pricing strategy that makes sure sales cover variable costs, with enough left over to contribute to both fixed expenses and profits. It can also be an invaluable tool for deciding which products may have the highest profitability, particularly when those products use equivalent resources. In general, the higher the contribution margin ratio, the better, with negative numbers indicating a loss on every unit produced. Using this formula, the contribution margin can be calculated for total revenue or for revenue per unit.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
We would consider the relevant range to be between one and eight passengers, and the fixed cost in this range would be \(\$200\). If they exceed the initial relevant range, the fixed costs would increase to \(\$400\) for nine to sixteen passengers. If the contribution margin for an ink pen is higher than that of a ball pen, the former will be given production preference owing to its higher profitability potential. Such decision-making is common to companies that manufacture a diversified portfolio of products, and management must allocate available resources in the most efficient manner to products with the highest profit potential. The contribution margin can help company management select from among several possible products that compete to use the same set of manufacturing resources. Say that a company has a pen-manufacturing machine that is capable of producing both ink pens and ball-point pens, and management must make a choice to produce only one of them.
How do you find the contribution margin per direct labor hour?
The contribution margin is computed as the selling price per unit, minus the variable cost per unit. Also known as dollar contribution per unit, the measure indicates how a particular product contributes to the overall profit of the company. The contribution margin is the leftover revenue after variable costs have been covered and it is used to contribute to fixed costs. If the fixed costs have also been paid, the remaining revenue is profit.
- Fixed and variable costs are expenses your company accrues from operating the business.
- However, the contribution margin facilitates product-level margin analysis on a per-unit basis, contrary to analyzing profitability on a consolidated basis in which all products are grouped together.
- It’s an important metric that compares a company’s overall profit to its sales.
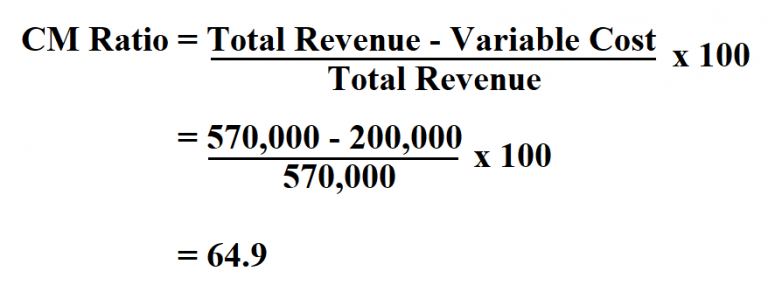
Formula to Calculate Contribution Margin Ratio
Contribution format income statements can be drawn up with data from more than one year’s income statements, when a person is interested in tracking contribution margins over time. Perhaps even more usefully, they can be drawn up for each product line or service. Here’s an example, showing a breakdown of Beta’s three main product lines. Knowing how to calculate the contribution margin is an invaluable skill for managers, as using it allows for the easy computation of break-evens and target income sales.
When comparing the two statements, take note of what changed and what remained the same from April to May. Use contribution margin alongside gross profit margin, your balance sheet, and other financial metrics and analyses. This is the only real way to determine whether your company is profitable in the short and long term and if you need to make widespread changes to your profit models.
How to Calculate the Contribution Margin Ratio
This demonstrates that, for every Cardinal model they sell, they will have $60 to contribute toward covering fixed costs and, if there is any left, toward profit. Every product that a company manufactures or every service a company provides will have a unique contribution margin per unit. In these examples, the contribution margin per unit was calculated in dollars per unit, but another way to calculate contribution margin is as a ratio (percentage).
The company will use this “margin” to cover fixed expenses and hopefully to provide a profit. In our example, the sales revenue from one shirt is $15 and the variable cost of one shirt is $10, so the individual contribution margin is $5. This $5 contribution margin is assumed to first cover fixed costs first and then realized as profit.
These costs may be higher because technology is often more expensive when it is new than it will be in the future, when it is easier and more cost-effective to produce and also more accessible. A good example of the change in cost of a new technological innovation over time is the personal computer, which was very expensive when it was first accounting facts developed but has decreased in cost significantly since that time. The same will likely happen over time with the cost of creating and using driverless transportation. Yes, the Contribution Margin Ratio is a useful measure of profitability as it indicates how much each sale contributes to covering fixed costs and producing profits.
Comentários